Theses
-
Continuous optimization of an IT environment (MSc)
Teemu Mikkonen, ongoing
(abstract)
Until very recently, servers were optimized for high-availability due to the fact that their optimization affected big number of users. Optimization of individual workstations using telemetry data is the next logical step to increase overall availability of an IT environment contributing to increased productivity of users. Computer malfunctions ruin productivity by wasting time of user, his/her collegues and also by affecting subsequent task performance due to irritation. Thesis is going to develop, test and propose processes and methods for detecting anomalies in workstation environments which are then resolved by IT experts
-
Food Object Detection and Recognition with Region Proposal Networks (MSc)
Janaki Koirala, ongoing
-
Emotion-based Recommender System for City Visitors built on analyzing Egocentric Images (BSc)
Andreas Hitz, ongoing
(abstract)(pdf)
 This thesis designs and implements a recommender system for city visitors, which is based on the analysis of emotions of pictures as well as the user’s location and own emotion.
Following a comprehensive literature review of related work on recommender systems, computer vision and emotion analysis, a conceptional architecture for the recommender system is designed and described step by step, covering all technical implementation
details, such as used algorithms, libraries and technologies. Firstly, databases of pictures collected from different sources are created. The contents of these photos are analyzed to receive a textual content description and identify the emotion of an image. Each image is, in addition to its extracted associated information, tagged with an emotion score, which is based on the two dimensions pleasure and activity. Secondly, the Python-based recommender system generates personalized recommendations for places to visit by using these scores together with the user’s location and emotion. A graphical user interface written in HTML and JavaScript serves as the base for accessing the system, where the pictures are marked on an interactive map, the user specifies his own location and emotion, and the recommendations can be retrieved.
The thesis continues with an evaluation of the system by performing a user study which demonstrates the usefulness of considering emotions for recommendations. It ends with a discussion about challenges, a view on future work, and a conclusive summary of the topic.
This thesis designs and implements a recommender system for city visitors, which is based on the analysis of emotions of pictures as well as the user’s location and own emotion.
Following a comprehensive literature review of related work on recommender systems, computer vision and emotion analysis, a conceptional architecture for the recommender system is designed and described step by step, covering all technical implementation
details, such as used algorithms, libraries and technologies. Firstly, databases of pictures collected from different sources are created. The contents of these photos are analyzed to receive a textual content description and identify the emotion of an image. Each image is, in addition to its extracted associated information, tagged with an emotion score, which is based on the two dimensions pleasure and activity. Secondly, the Python-based recommender system generates personalized recommendations for places to visit by using these scores together with the user’s location and emotion. A graphical user interface written in HTML and JavaScript serves as the base for accessing the system, where the pictures are marked on an interactive map, the user specifies his own location and emotion, and the recommendations can be retrieved.
The thesis continues with an evaluation of the system by performing a user study which demonstrates the usefulness of considering emotions for recommendations. It ends with a discussion about challenges, a view on future work, and a conclusive summary of the topic.
- Walking Speed detection from 5G Prototype System (MSc)
Bahareh Gholampooryazdi, 05.2017
(abstract)(pdf)
 While most RF-sensing approaches proposed in the literature rely on short-distance
indoor point-to-point instrumentations, actual large-scale installation of RF sensing
suggests the use of ubiquitously available cellular systems. In particular, the 5th
generation of the wireless communication standard (5G) is envisioned as a universal
communication means also for Internet of Things devices.
This thesis presents an investigation of device-free environmental perception capa-
bilities in a 5G prototype system in two cases; walking speed and human presence
detection, and elaborate a comparison with the former case and acceleration sensing
analysis. This thesis attempts to analyze the perception capabilities of 5G system
in order to recognize human mostly common activities and presence detection near
transceiver devices which the instrumentation exploits a device-free system capable
of detect activities without carrying devices capitalizing on environmental RF-noise.
This is done via the study of existing and related literature. After that, the imple-
mentation and evaluation of walking speed and presence detection is described in
details. In addition, evaluation consists of utilizing a prototypical 5G system with
52 OFDM carriers over 12.48 MHz bandwidth at 3.45 GHz, which we consider
the impact of the number and choice of channels and compare the recognition
performance with acceleration-based sensing. It was concluded that in realistic
settings with five subjects, accurate recognition of activities and environmental
situations can be a reliable implicit service of future 5G installations.
While most RF-sensing approaches proposed in the literature rely on short-distance
indoor point-to-point instrumentations, actual large-scale installation of RF sensing
suggests the use of ubiquitously available cellular systems. In particular, the 5th
generation of the wireless communication standard (5G) is envisioned as a universal
communication means also for Internet of Things devices.
This thesis presents an investigation of device-free environmental perception capa-
bilities in a 5G prototype system in two cases; walking speed and human presence
detection, and elaborate a comparison with the former case and acceleration sensing
analysis. This thesis attempts to analyze the perception capabilities of 5G system
in order to recognize human mostly common activities and presence detection near
transceiver devices which the instrumentation exploits a device-free system capable
of detect activities without carrying devices capitalizing on environmental RF-noise.
This is done via the study of existing and related literature. After that, the imple-
mentation and evaluation of walking speed and presence detection is described in
details. In addition, evaluation consists of utilizing a prototypical 5G system with
52 OFDM carriers over 12.48 MHz bandwidth at 3.45 GHz, which we consider
the impact of the number and choice of channels and compare the recognition
performance with acceleration-based sensing. It was concluded that in realistic
settings with five subjects, accurate recognition of activities and environmental
situations can be a reliable implicit service of future 5G installations.
- Transfer learning in emotion recognition (BSc)
Niklas Strengell, 05.2017
(abstract)(pdf)
 The purpose of this thesis is to review and discuss automated emotion recognition and transfer learning. Firstly, emotional theories are discussed and the various modalities from which emotions can be recognized are introduced. Secondly, transfer learning, which is a machine learning technique for transferring previously learned knowledge, is discussed and explained in detail. Lastly, new research which exploits transfer learning techniques in automated emotion recognition is reviewed and the future of research is discussed.
The purpose of this thesis is to review and discuss automated emotion recognition and transfer learning. Firstly, emotional theories are discussed and the various modalities from which emotions can be recognized are introduced. Secondly, transfer learning, which is a machine learning technique for transferring previously learned knowledge, is discussed and explained in detail. Lastly, new research which exploits transfer learning techniques in automated emotion recognition is reviewed and the future of research is discussed.
-
Blockchain as a distributed database for edge-supported IoT (BSc)
Juuso Mikkonen, ongoing
(abstract)
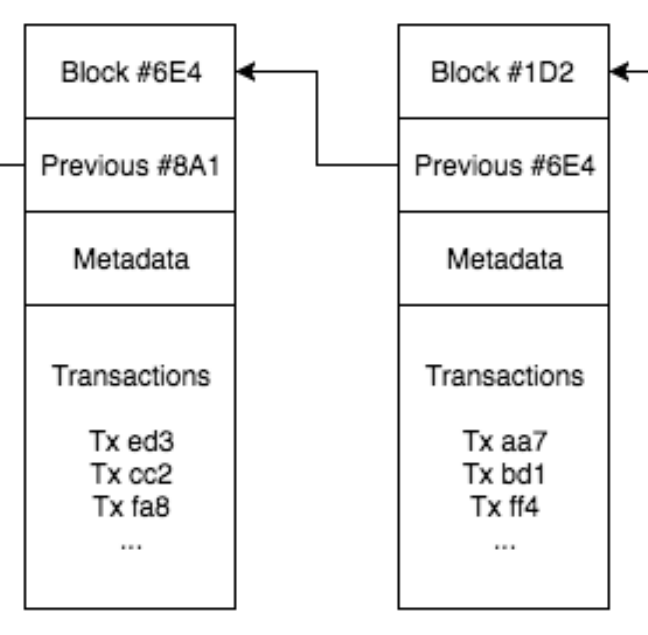 Internet of Things (IoT) is an emerging trend in many industrial and consumer applications. IoT inherently
poses new challenges to technical implementations due to its distributed nature and large amounts of
gathered data.
A fundamental challenge that must be addressed in IoT applications is the storage of data gathered by edge devices in the network. The devices themselves are typically not very performant and have little capacity to store data. Industrial IoT device networks of large amounts of edge devices can extract new data at a very high rate. The data can be a key element of the business logic of the IoT network. A distributed database implemented utilizing blockchain technology is one option for IoT data
storage. Decentralized nature and inherent security are traits that make the technology an appealing choice for distributed storage. Blockchain technology also poses some challenges not faced by more traditional distributed databases. Current implementations like the Bitcoin protocol are severely limited by their performance. Most often there exists a trade-off situation between throughput and latency. Recent development in the field of blockchain technology has brought many possible improvements to the blockchain model. The utilization of new protocols could potentially solve many of the scalability issues and trade-offs inherent to previous technologies. This would in turn enable the use of blockchain in many large-scale industrial applications.
A successful solution to IoT edge storage would have a big effect on industrial IoT solutions. It would enable the use of cheaper and more simple devices while simultaneously extending the size of device networks. The security of the solutions could also be improved in the process enabling the use of IoT in fields with high privacy requirements.
Internet of Things (IoT) is an emerging trend in many industrial and consumer applications. IoT inherently
poses new challenges to technical implementations due to its distributed nature and large amounts of
gathered data.
A fundamental challenge that must be addressed in IoT applications is the storage of data gathered by edge devices in the network. The devices themselves are typically not very performant and have little capacity to store data. Industrial IoT device networks of large amounts of edge devices can extract new data at a very high rate. The data can be a key element of the business logic of the IoT network. A distributed database implemented utilizing blockchain technology is one option for IoT data
storage. Decentralized nature and inherent security are traits that make the technology an appealing choice for distributed storage. Blockchain technology also poses some challenges not faced by more traditional distributed databases. Current implementations like the Bitcoin protocol are severely limited by their performance. Most often there exists a trade-off situation between throughput and latency. Recent development in the field of blockchain technology has brought many possible improvements to the blockchain model. The utilization of new protocols could potentially solve many of the scalability issues and trade-offs inherent to previous technologies. This would in turn enable the use of blockchain in many large-scale industrial applications.
A successful solution to IoT edge storage would have a big effect on industrial IoT solutions. It would enable the use of cheaper and more simple devices while simultaneously extending the size of device networks. The security of the solutions could also be improved in the process enabling the use of IoT in fields with high privacy requirements.
-
Application of Internet of Things Framework On Enhanced Lean Construction Management (MSc)
Dinesh Hyaunmikha, ongoing
(abstract)
 Internet of things is an ever emerging field with its application growing in all areas. Smart housing and smart cities are some of them with intelligent products and connected devices through internet. Currently, research is extending towards application of IoT communication framework for automation of production control in construction industry as well.
Information flow and synchronization between site teams, managers, various contractors and suppliers still remains a major factor of delay in construction workflow. Construction management systems, such as “VisiLean” tries to overcome some of these overheads by providing a visual model (BIM – “Building Information Model”) along with the management workflow.
This main aim of this thesis is to study the practical applications of IoT communication framework on construction management systems on scenarios such as automated procurement, tracking resources or production planning and control. Such information would then be represented in the relevant part in the BIM automatically.
Internet of things is an ever emerging field with its application growing in all areas. Smart housing and smart cities are some of them with intelligent products and connected devices through internet. Currently, research is extending towards application of IoT communication framework for automation of production control in construction industry as well.
Information flow and synchronization between site teams, managers, various contractors and suppliers still remains a major factor of delay in construction workflow. Construction management systems, such as “VisiLean” tries to overcome some of these overheads by providing a visual model (BIM – “Building Information Model”) along with the management workflow.
This main aim of this thesis is to study the practical applications of IoT communication framework on construction management systems on scenarios such as automated procurement, tracking resources or production planning and control. Such information would then be represented in the relevant part in the BIM automatically.
 This thesis designs and implements a recommender system for city visitors, which is based on the analysis of emotions of pictures as well as the user’s location and own emotion.
Following a comprehensive literature review of related work on recommender systems, computer vision and emotion analysis, a conceptional architecture for the recommender system is designed and described step by step, covering all technical implementation
details, such as used algorithms, libraries and technologies. Firstly, databases of pictures collected from different sources are created. The contents of these photos are analyzed to receive a textual content description and identify the emotion of an image. Each image is, in addition to its extracted associated information, tagged with an emotion score, which is based on the two dimensions pleasure and activity. Secondly, the Python-based recommender system generates personalized recommendations for places to visit by using these scores together with the user’s location and emotion. A graphical user interface written in HTML and JavaScript serves as the base for accessing the system, where the pictures are marked on an interactive map, the user specifies his own location and emotion, and the recommendations can be retrieved.
The thesis continues with an evaluation of the system by performing a user study which demonstrates the usefulness of considering emotions for recommendations. It ends with a discussion about challenges, a view on future work, and a conclusive summary of the topic.
This thesis designs and implements a recommender system for city visitors, which is based on the analysis of emotions of pictures as well as the user’s location and own emotion.
Following a comprehensive literature review of related work on recommender systems, computer vision and emotion analysis, a conceptional architecture for the recommender system is designed and described step by step, covering all technical implementation
details, such as used algorithms, libraries and technologies. Firstly, databases of pictures collected from different sources are created. The contents of these photos are analyzed to receive a textual content description and identify the emotion of an image. Each image is, in addition to its extracted associated information, tagged with an emotion score, which is based on the two dimensions pleasure and activity. Secondly, the Python-based recommender system generates personalized recommendations for places to visit by using these scores together with the user’s location and emotion. A graphical user interface written in HTML and JavaScript serves as the base for accessing the system, where the pictures are marked on an interactive map, the user specifies his own location and emotion, and the recommendations can be retrieved.
The thesis continues with an evaluation of the system by performing a user study which demonstrates the usefulness of considering emotions for recommendations. It ends with a discussion about challenges, a view on future work, and a conclusive summary of the topic.
 While most RF-sensing approaches proposed in the literature rely on short-distance
indoor point-to-point instrumentations, actual large-scale installation of RF sensing
suggests the use of ubiquitously available cellular systems. In particular, the 5th
generation of the wireless communication standard (5G) is envisioned as a universal
communication means also for Internet of Things devices.
This thesis presents an investigation of device-free environmental perception capa-
bilities in a 5G prototype system in two cases; walking speed and human presence
detection, and elaborate a comparison with the former case and acceleration sensing
analysis. This thesis attempts to analyze the perception capabilities of 5G system
in order to recognize human mostly common activities and presence detection near
transceiver devices which the instrumentation exploits a device-free system capable
of detect activities without carrying devices capitalizing on environmental RF-noise.
This is done via the study of existing and related literature. After that, the imple-
mentation and evaluation of walking speed and presence detection is described in
details. In addition, evaluation consists of utilizing a prototypical 5G system with
52 OFDM carriers over 12.48 MHz bandwidth at 3.45 GHz, which we consider
the impact of the number and choice of channels and compare the recognition
performance with acceleration-based sensing. It was concluded that in realistic
settings with five subjects, accurate recognition of activities and environmental
situations can be a reliable implicit service of future 5G installations.
While most RF-sensing approaches proposed in the literature rely on short-distance
indoor point-to-point instrumentations, actual large-scale installation of RF sensing
suggests the use of ubiquitously available cellular systems. In particular, the 5th
generation of the wireless communication standard (5G) is envisioned as a universal
communication means also for Internet of Things devices.
This thesis presents an investigation of device-free environmental perception capa-
bilities in a 5G prototype system in two cases; walking speed and human presence
detection, and elaborate a comparison with the former case and acceleration sensing
analysis. This thesis attempts to analyze the perception capabilities of 5G system
in order to recognize human mostly common activities and presence detection near
transceiver devices which the instrumentation exploits a device-free system capable
of detect activities without carrying devices capitalizing on environmental RF-noise.
This is done via the study of existing and related literature. After that, the imple-
mentation and evaluation of walking speed and presence detection is described in
details. In addition, evaluation consists of utilizing a prototypical 5G system with
52 OFDM carriers over 12.48 MHz bandwidth at 3.45 GHz, which we consider
the impact of the number and choice of channels and compare the recognition
performance with acceleration-based sensing. It was concluded that in realistic
settings with five subjects, accurate recognition of activities and environmental
situations can be a reliable implicit service of future 5G installations.
 The purpose of this thesis is to review and discuss automated emotion recognition and transfer learning. Firstly, emotional theories are discussed and the various modalities from which emotions can be recognized are introduced. Secondly, transfer learning, which is a machine learning technique for transferring previously learned knowledge, is discussed and explained in detail. Lastly, new research which exploits transfer learning techniques in automated emotion recognition is reviewed and the future of research is discussed.
The purpose of this thesis is to review and discuss automated emotion recognition and transfer learning. Firstly, emotional theories are discussed and the various modalities from which emotions can be recognized are introduced. Secondly, transfer learning, which is a machine learning technique for transferring previously learned knowledge, is discussed and explained in detail. Lastly, new research which exploits transfer learning techniques in automated emotion recognition is reviewed and the future of research is discussed.
 Internet of Things (IoT) is an emerging trend in many industrial and consumer applications. IoT inherently
poses new challenges to technical implementations due to its distributed nature and large amounts of
gathered data.
A fundamental challenge that must be addressed in IoT applications is the storage of data gathered by edge devices in the network. The devices themselves are typically not very performant and have little capacity to store data. Industrial IoT device networks of large amounts of edge devices can extract new data at a very high rate. The data can be a key element of the business logic of the IoT network. A distributed database implemented utilizing blockchain technology is one option for IoT data
storage. Decentralized nature and inherent security are traits that make the technology an appealing choice for distributed storage. Blockchain technology also poses some challenges not faced by more traditional distributed databases. Current implementations like the Bitcoin protocol are severely limited by their performance. Most often there exists a trade-off situation between throughput and latency. Recent development in the field of blockchain technology has brought many possible improvements to the blockchain model. The utilization of new protocols could potentially solve many of the scalability issues and trade-offs inherent to previous technologies. This would in turn enable the use of blockchain in many large-scale industrial applications.
A successful solution to IoT edge storage would have a big effect on industrial IoT solutions. It would enable the use of cheaper and more simple devices while simultaneously extending the size of device networks. The security of the solutions could also be improved in the process enabling the use of IoT in fields with high privacy requirements.
Internet of Things (IoT) is an emerging trend in many industrial and consumer applications. IoT inherently
poses new challenges to technical implementations due to its distributed nature and large amounts of
gathered data.
A fundamental challenge that must be addressed in IoT applications is the storage of data gathered by edge devices in the network. The devices themselves are typically not very performant and have little capacity to store data. Industrial IoT device networks of large amounts of edge devices can extract new data at a very high rate. The data can be a key element of the business logic of the IoT network. A distributed database implemented utilizing blockchain technology is one option for IoT data
storage. Decentralized nature and inherent security are traits that make the technology an appealing choice for distributed storage. Blockchain technology also poses some challenges not faced by more traditional distributed databases. Current implementations like the Bitcoin protocol are severely limited by their performance. Most often there exists a trade-off situation between throughput and latency. Recent development in the field of blockchain technology has brought many possible improvements to the blockchain model. The utilization of new protocols could potentially solve many of the scalability issues and trade-offs inherent to previous technologies. This would in turn enable the use of blockchain in many large-scale industrial applications.
A successful solution to IoT edge storage would have a big effect on industrial IoT solutions. It would enable the use of cheaper and more simple devices while simultaneously extending the size of device networks. The security of the solutions could also be improved in the process enabling the use of IoT in fields with high privacy requirements.
